Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia in Newborns
Introduction
The birth of a newborn is a moment of immense joy and anticipation for parents and families. However, sometimes, unexpected health issues may arise, challenging the happiness of this occasion. One such condition is Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH), a rare but serious congenital anomaly that affects newborns. In this blog, we will explore what CDH is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, with insights from Dr. Apoorva Kulkarni, a renowned pediatric surgeon in Bandra and Thane.
What is Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH)?
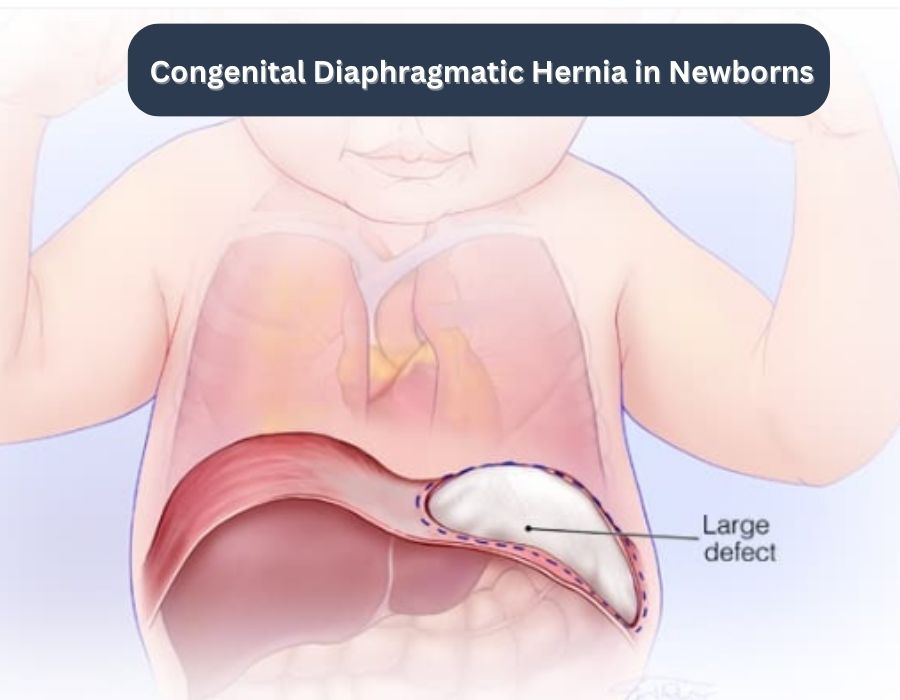
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia is a birth defect that occurs when there is a hole or gap in the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. This opening allows abdominal organs, such as the stomach, liver, and intestines, to move into the chest cavity, crowding the lungs and hampering their development. As a result, CDH can lead to severe respiratory problems after birth.
Causes of CDH
The exact cause of CDH is not always clear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some possible causes and risk factors include:
- Genetic Factors: CDH may run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Mutations in certain genes have been linked to the development of this condition.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins or medications during pregnancy may increase the risk of CDH.
- Multifactorial Inheritance: In some cases, CDH may result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Symptoms of CDH
The symptoms of CDH can vary in severity, but they often include:
- Difficulty breathing: Newborns with CDH may have rapid, shallow breathing and may require assistance with ventilation immediately after birth.
- Cyanosis (bluish skin color): Due to inadequate oxygen levels in the blood, affected babies may appear blue
- Abdominal Distension: The abdomen may appear larger than normal due to abdominal organs in the chest cavity.
- Feeding difficulties: CDH can make it challenging for newborns to feed and gain weight.
Diagnosis of CDH
Prenatal diagnosis of CDH is possible through ultrasound imaging during pregnancy. If CDH is suspected, a detailed fetal ultrasound or a fetal MRI can provide valuable information about the condition and its severity. After birth, a physical examination, chest X-rays, and echocardiography are commonly used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for CDH
Treatment for CDH typically involves a multidisciplinary approach and depends on the severity of the condition. It may include:
- Immediate Stabilization: Newborns with severe CDH may require intubation and mechanical ventilation to support their breathing.
- Surgery: Most infants with CDH require surgical repair to close the diaphragmatic defect and return the abdominal organs to their proper place. This procedure is usually performed in the first few days or weeks of life.
- Long-Term Care: After surgery, infants with CDH often require ongoing medical care, including respiratory support and monitoring of their growth and development.
Conclusion
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia is a challenging condition that affects newborns and their families. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many infants with CDH can lead healthy lives. Dr. Apoorva Kulkarni, a pediatric surgeon in Bandra and Thane, has dedicated his career to providing expert care to children with CDH and other congenital anomalies. His expertise and compassion have made a significant difference in the lives of countless families facing the challenges of CDH. If you have concerns about CDH or any other pediatric surgical condition, Dr. Apoorva Kulkarni is a trusted resource for expert guidance and care.
Latest Blogs
What Is Fundoplication Surgery in Children? A Parent’s Complete Guide
Posterior Urethral Valve (PUV): A Serious Urological Condition in Boys

Blood in Urine (Hematuria) in Kids — What’s Normal and What’s an Emergency?
Preputioplasty: A Safe Alternative to Circumcision for Tight Foreskin in Children

Challenges in Paediatric Laparoscopic Surgeries

